Esperienza di piegatura della lamiera
A: Ione di tonnellaggio della macchina piegatubi
Durante il processo di piegatura, la forza tra gli stampi superiore e inferiore viene applicata al materiale, causando la deformazione plastica del materiale. Il tonnellaggio di lavoro si riferisce alla pressione di flessione durante la flessione. I fattori che influenzano la determinazione del tonnellaggio di lavoro sono: raggio di curvatura, metodo di curvatura, rapporto dello stampo, lunghezza del gomito, spessore e resistenza del materiale di curvatura, ecc.
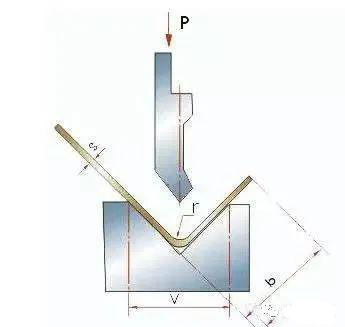
Generalmente, il tonnellaggio di lavoro può essere modificato secondo la tabella seguente e impostato nei parametri di elaborazione.
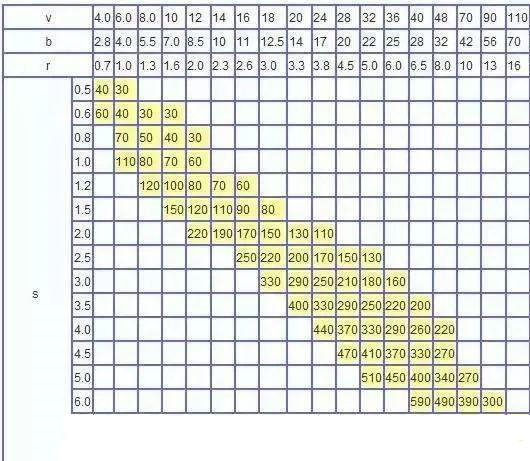
1. Il valore nella tabella è la pressione di piegatura quando la lunghezza del foglio è di un metro:
Esempio: S = 4mm L = 1000mm V = 32mm
Cerca la tabella e ottieni P = 330kN
2. Questa tabella è calcolata in base al materiale con resistenza σb = 450 N / mm2. Quando si piegano altri materiali, la pressione di piegatura è il prodotto dei dati nella tabella e dei seguenti coefficienti;
Bronzo (morbido): 0,5;
Acciaio inossidabile: 1,5;
Alluminio (morbido): 0,5;
Acciaio al cromo-molibdeno: 2.0.
3. Formula di calcolo approssimativa della pressione di flessione
P = 650s2L / 1000v
P - kn
S - mm
L - mm
V - mm
Tabella comparativa della pressione di flessione
B. Problemi comuni nella flessione della lamiera
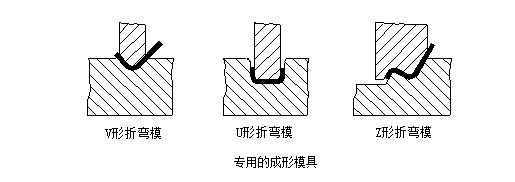
1) Stampi di piegatura comunemente usati
Stampo di piegatura comunemente usato, come mostrato di seguito. Al fine di prolungare la durata dello stampo, le parti sono progettate con angoli arrotondati il più possibile.
Se l'altezza della flangia è troppo piccola, anche l'uso di una matrice di piegatura non favorisce la formazione. Generalmente, l'altezza della flangia L≥3t (incluso lo spessore della parete).
Metodo di elaborazione dei passaggi
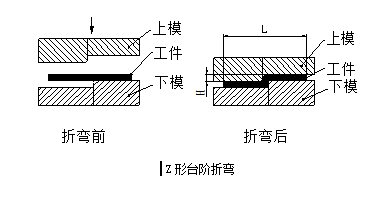
For some low-profile sheet metal Z-shaped step bending, processing manufacturers often use simple molds to process on punches or hydraulic presses, and small batches can also be processed on the bending machine with stepped die, as shown in the following figure. However, the height H should not be too high, generally should be (0 ~ 1.0) t, if the height is (1.0 ~ 4.0) t, it is necessary to consider the use of the mold form of the addition and discharge structure according to actual conditions.
The height of this mold step can be adjusted by adding shims, so the height H can be adjusted arbitrarily, but there is also a disadvantage that the length L size is not easy to guarantee, and the verticality of the vertical side is not easy to guarantee. If the height H size is large, it is necessary to consider bending on the bending machine.
Esistono due tipi di piegatrice: piegatrice ordinaria e piegatrice CNC. A causa dei requisiti di alta precisione e delle forme di piegatura irregolari, la piegatura della lamiera delle apparecchiature di comunicazione è generalmente piegata con una macchina piegatrice CNC. Il principio di base è utilizzare il coltello piegatore (matrice superiore) e la scanalatura a V (inferiore) della macchina piegatrice. Die), piegare e formare parti in lamiera.
Vantaggi: serraggio conveniente, posizionamento accurato e velocità di elaborazione rapida;
Svantaggi: bassa pressione, può solo elaborare una formatura semplice e bassa efficienza.
Principi di base della formazione
Il principio di base della formazione è mostrato nella figura seguente:
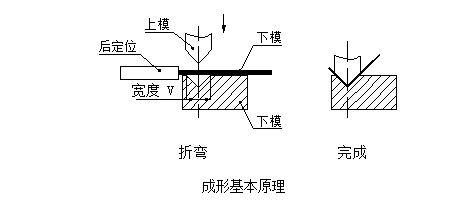
Coltello da flessione (matrice superiore)
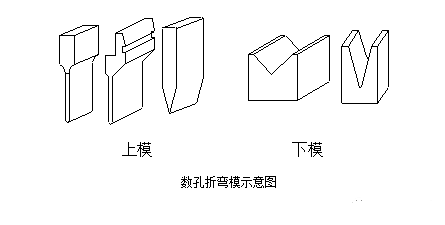
The form of the bending knife is shown in the figure below. It is mainly ed according to the shape of the workpiece during processing. Generally, there are many bending knife shapes of processing manufacturers, especially those with a high degree of specialization. In order to process various complex bending , Bending knives of many shapes and specifications are customized.
The lower die generally uses V = 6t (t is the material thickness) die.
There are many factors that affect the bending process, mainly including the radius of the upper die arc, material, material thickness, lower die strength, die size of the lower die and other factors. In order to meet the needs of the product, the manufacturer has already serialized the bending knife mold under the condition of ensuring the safety of the bending machine. We need to have a general understanding of the existing bending knife mold during the structural design process. See the figure below, the upper die is on the left and the lower die is on the right.
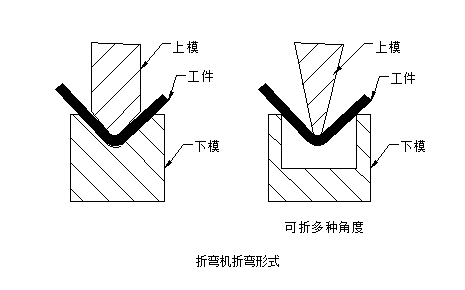
Basic principles of bending processing sequence:
(1) Bending from inside to outside;
(2) Bending from small to large;
(3) Bend the special shape first, and then bend the general shape;
(4) After the previous process is formed, it does not affect or interfere with the subsequent process.
The current bending form is generally shown in the following figure:
2) Bending radius
When bending sheet metal, a bending radius is required at the bending place. The bending radius should not be too large or too small, and should be ed appropriately. If the bending radius is too small, it is easy to cause cracking at the bending point, and if the bending radius is too large, the bending is easy to rebound. The preferred bending radius (inner bending radius) of various materials with different thicknesses is shown in the table below
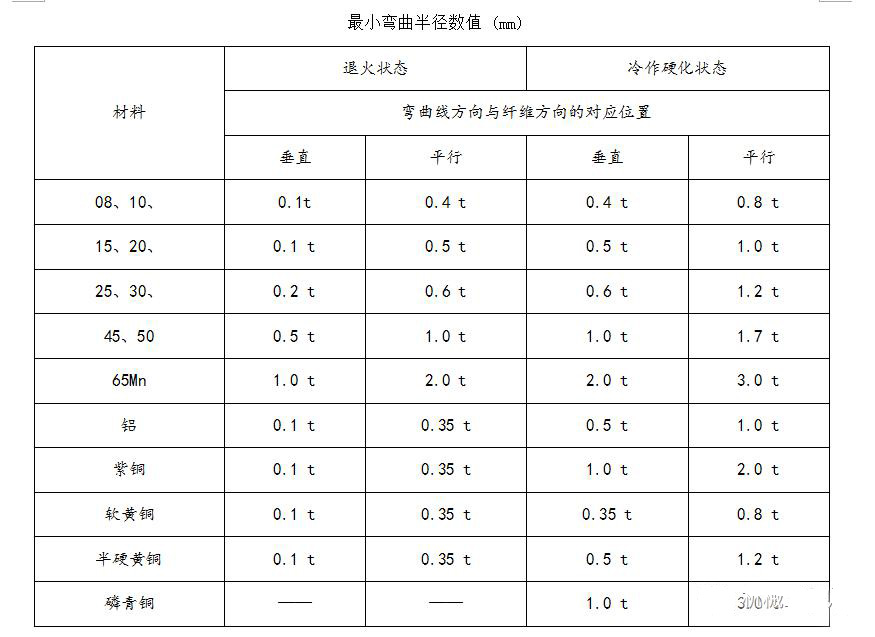
The data in the table above is the preferred data, for reference only. In fact, the corners of manufacturers' bending knives are usually 0.3, and a small number of bending knives are 0.5.
For ordinary low-carbon steel plate, rust-proof aluminum plate, brass plate, copper plate, etc., the inner fillet 0.2 is no problem, but for some high-carbon steel, hard aluminum, super hard aluminum, this bending round It will cause bending breakage or cracking of the outer corners.
3) Bending and rebound
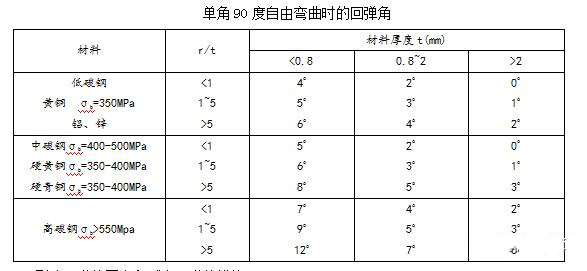
Springback angle Δα = b-a
Where b——the actual angle of the part after rebound;
a—The angle of the mold.
The size of the rebound angle
See the table below for the springback angle when a single angle is 90 ° free bending.
Factors affecting rebound and measures to reduce rebound
① The mechanical properties of the material The rebound angle is directly proportional to the yield point of the material and inversely proportional to the elastic modulus E. For sheet metal parts with high accuracy requirements, in order to reduce springback, the material should be ed as low-carbon steel as possible, not high-carbon steel and stainless steel.
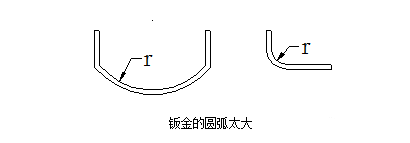
② The larger the relative bending radius r / t, the smaller the degree of deformation and the greater the rebound angle Δα. This is a relatively important concept. The rounded corners of sheet metal bending should be as small as possible, as long as the material properties allow, to improve accuracy. In particular, pay attention to avoid designing large arcs as much as possible, as shown in the following figure, such large arcs have greater difficulty in production and quality control:
4) Calculation of the minimum bending edge in one bending
The initial state of the L-shaped bend at the time of bending is shown below:
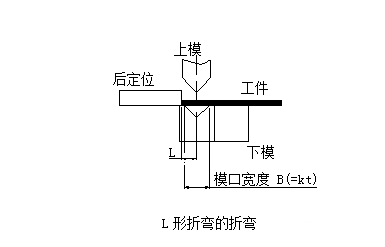
The initial state of the Z-shaped bending at the time of bending is shown in the figure below
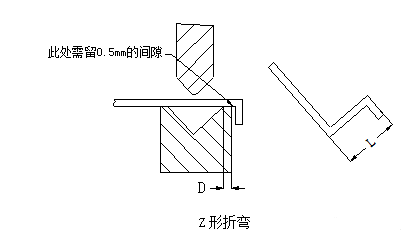
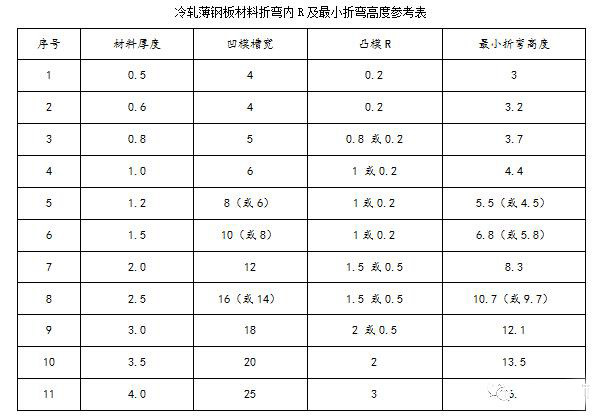
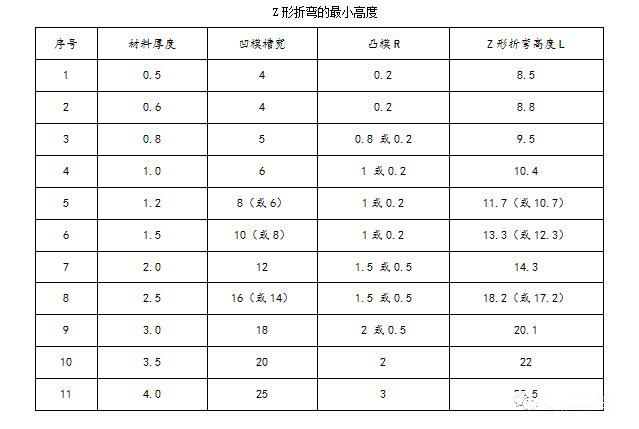
The minimum bending dimension L corresponding to the Z-bending of sheet metal with different material thickness is shown in the following table:
C. Fast calculation method of sheet metal bending and unfolding
When the sheet metal bending and flattening, one side of the material will be elongated and one side will be compressed. The factors affected are: material type, material thickness, material heat treatment and processing bending angle.
Expand calculation principle:
1) During the bending process, the outer layer is subjected to tensile stress and the inner layer is subjected to compressive stress. Between tension and compression, there is a transition layer that is neither tensile nor compressive, called the neutral layer; the neutral layer is bent during the bending process The length is the same as before bending, so the neutral layer is the benchmark for calculating the unfolded length of the bending piece.
2) The position of the neutral layer is related to the degree of deformation. When the bending radius is large and the bending angle is small, the degree of deformation is small. The position of the neutral layer is close to the center of the sheet thickness; when the bending radius becomes small, the bending angle increases When it is large, the degree of deformation increases accordingly, and the position of the neutral layer gradually moves to the inside of the bending center. The distance from the neutral layer to the inside of the sheet is expressed by λ.
On the other hand, with the emergence and popularization of computer technology, in order to make better use of the computer's super analysis and calculation capabilities, people increasingly use computer-aided design, but when computer programs simulate the bending of sheet metal Or it needs a calculation method in order to accurately simulate the process.
Although only to complete a certain calculation, each store can customize a specific program according to its original pinch rules, but nowadays, most commercial CAD and three-dimensional solid modeling systems have provided more general and Powerful solution.
Nella maggior parte dei casi, questi software applicativi possono anche essere compatibili con le regole originali basate sull'esperienza e pizzicare le dita e fornire un modo per personalizzare specifici contenuti di input al suo processo di calcolo. SolidWorks è diventato naturalmente leader nel fornire questa capacità di progettazione della lamiera.




